Japan share cordial and friendly relations with South Asia countries. The economic ties date back to British colonial era.
In the post-colonial era, when the regional diplomatic and political relations emerged more independently, these ties became even more strengthened.
During the World War-II, when the Axis powers knocked the doors of the Indo-Pakistan subcontinent, the British urged the locals to support them. The leaders of All India National Congress wanted to muster the support of the Japanese forces against the foreign yoke. The Muslims opposed the idea and denounced that one foreign power may replace other. Former launched Quit India movement in 1942 but soon wind began blowing in a different direction and the movement ended without any result.
The region of South Asia remained important for the superpowers during the period of the Cold War. In post-Cold War period, its importance continued unabated. It is the nucleus of China-Pakistan Economic Corridor.
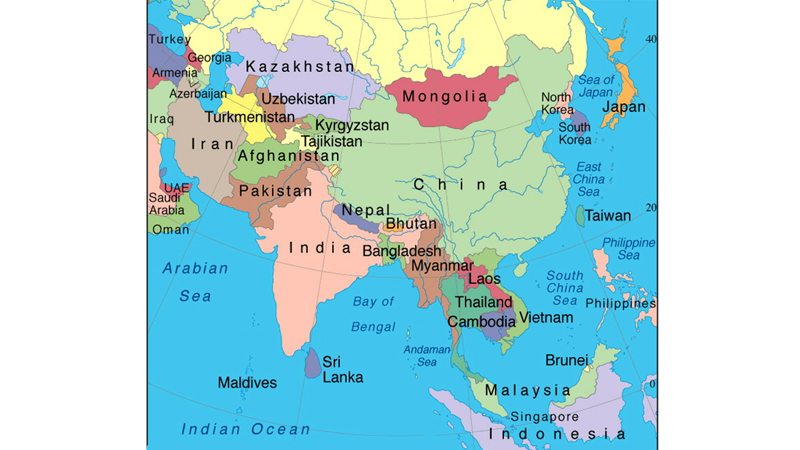
South Asia share borders with the regions of Central Asia, South East Asia and the Persian Gulf. It also shares waters of the Arabian Sea. It has close proximity to the Strait of Hormuz and Strait of Malacca. Former is the mouth of the Persian Gulf through which oil is exported to the western countries and Japan. Latter connects the Indian Ocean with the Pacific Ocean. There is popular saying that the Indian Ocean is Ocean of the future and one which would have an influence on it will rule the world. Strait of Malacca is also important for the sea traffic.
The Strait of Hormuz is a narrow strip of water. It connects the Persian Gulf with the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman. It is thirty-three to 90 kilometres in length. Its mouth is about three-kilometres wide. During eight years of Iran-Iraq war, both countries wanted to have control over it once Iran threatened to close the strait when Iraq created disturbance in traffic of ships there.
The western and other countries including Japan import oil from the countries located around the Persian Gulf. The ships carrying oil passes near the seaports of South Asia. From Strait of Hormuz, the ships enter Strait of Malacca and then travel to the different countries. Thus, the region of South Asia is crucial for the oil importing countries.
There are also other factors which contribute to the importance of South Asia. Firstly, the mankind survived on the land of South Asia even five thousand years ago. The ruins of Moen-jo-Daro near district Larkana of the province of Sindh and that of Harappa near district Sahiwal of the province of Punjab is witness to this fact. The ruins display that people were civilised and possessed a sense of civic amenities, proper municipal governance and peaceful and the welfare state.
Secondly, the great conquerors of the world came here. Alexander and other warriors and conquerors used to recruit people for their respective army and conquered the world;
Secondly, Silk Road started from China, passed through the territory of South Asia and reached to Japan and the land of Europe. It brought Buddhism to China and Japan. Moreover, the preachers of the religions of Judaism, Christianity, Zoroastrianism and Islam used this Road for bringing their message to other parts of the world.
Thirdly, after the inclusion of Afghanistan in the region of South Asia it shares common borders with the Central Asian Republics. These Muslim states declared their respective independence from the former Union of Soviet Socialist Republic. Their untapped natural resources are not less important than those of the Persian Gulf. Rather they possess more value as these resources have not been fully utilised. The wiping out natural resources of the Middle East countries increases the importance of the natural resources of CARs.
The world is turning to non-traditional sources of electricity production. The reserves of uranium in the region of Central Asia may meet the requirements of countries looking for producing electricity. Japan’s main source of producing electricity is nuclear reactors. Thus, uranium is important for it.
Fourthly, the disunion of the Soviet Union has ushered new Great Game in the region. Afghanistan is its main ground. The world powers are competing to have, at least, their respective interests secured;
Lastly, the region of South Asia has received new geostrategic turn after launching of CPEC. Gwadar is being developed as the nucleus of the corridor. In response, Iran and India are developing Chabahar seaport. This competition between China and its informal allies and the countries in competition may further increase the importance of the region in world affairs.
Bilateral relations always base on mutual response. Both the countries want to achieve interests through help and giving relaxation, to some extent, to each other. Japan has the following interests in the region of South Asia:
Firstly, Japan has cultural and religious attachment with South Asia. It received Buddhism from this region which is its main religion. When the Taliban government destroyed the statues of Buddha in Afghanistan, the government of Japan protested against it. However, it did not relinquish its relations with post Taliban Afghanistan;
Secondly; the region is vulnerable due to nuclear armament. India undertook its first nuclear explosion in 1974 which created tension in the region. It attracted the attention of the world powers. India again went for the atomic explosion in 1999. It tilted the balance of power in favour of India in the region. Pakistan felt insecure. Thus, it decided to opt for the nuclear explosion. Japan condemned the nuclear race between two rival countries. It held Kashmir as a flash point;
Japan is only victim of nuclear terrorism of the United States. Its two cities Hiroshima and Nagasaki were bombed by the U.S in World War II on 6th and 9th August, 1945 respectively. Japan know the consequences and loss of nuclear armament. Thus, it wants to end nuclearisation of South Asia;
Thirdly, the population of the region is more than 1.7 billion. It is ideal market for the consumption of Japanese goods and commodities. According to the website of Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Japan, the balance of trade between Japan and different countries of South Asia is as under:
Country Trade volume
Bangladesh (2015)
Export 1,081m USD
Import 1,373m USD
Bhutan (2014)
Export 199 million yen
Import 1709 million yen
India (2016)
Export 509 billion yen
Import 889 billion yen
Maldives (2015)
Export 1.26 billion yen
Import 2.14 billion yen
Nepal (2015/2016)
Export Rs 1.2 billion
Import Rs 6 billion
Pakistan (2015)
Export 236 million yen
Import 1.84 billion yen
The figures mentioned above clearly indicates that balance of trade is in favor of Japan. It may not afford to ignore the region and leave such favorable volume of trade;
Thirdly, Japan’s Foreign Direct Investment is in billions of US dollars. According to aforementioned source, the FDI in different countries of the region is as under:
Name of Country Amount of FDI
Bangladesh 96.3m USD (2014)
India 465 billion yen (2016)
Nepal Rs 223.40 m (2015-16)
Pakistan 30.1 m USD (2014-15)
Moreover, the Japanese companies have also invested in different sectors in the region. The country earns huge amount which have substantial part in making Japan third world economy.
Fourthly, Japan has concerns about law and order situation in the region. It wants peace there. The region inherited the problem of Kashmir from the British legacy. The United Nations passed Resolution for recognising and extending right of self-determination to the Kashmiris. The first Prime Minister of India, Jawaharlal Nehru accepted to implement the UN resolution.
During World War-II, the Axis powers knocked the doors subcontinent. The leaders of All India National Congress wanted to muster support of the Japanese forces against the British imperial yoke. Muslims opposed the idea, worried that a new foreign power may replace the old one
But later on, he turned away from his commitment. India and Pakistan have fought two full-fledged wars in 1948 and 1965 and half war in 1999 on the front of Kargil. Both the countries have strained relations which is detrimental to the peace of the region of South Asia. Japan offered to hold international conference on the problem of Kashmir. India turned down the proposal. Unless peace remains intact, Japan’s economic interests will be secure in the region;
Fifthly, row between China and India brought Japan close to India. Japan has territorial issue with China. Due to this, Japan feels natural ally of India. Both the countries along with Brazil and South Africa formed informal group to support each other for permanent representation in the Security Council of the United Nations;
Sixthly, India wants to emerge as an Asian power. It considers itself as spokesperson of South Asia. This concept has turned India in self deception. Japan gives weight to the Indian territorial and military size;
Seventhly, India claims to be the largest democratic country of the world. Japan also views it with respect;
Eighthly, the South Asia Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) came into being in 1985. Initially, it represented the seven countries of the region. Later on, Afghanistan was also admitted in the Association. It is a non-political and economic and socio-cultural organisation. The world powers and other countries have status of observer in SAARC. These include the United States, China, European Union, Japan, Burma, South Korea, Australia, Iran and Mauritius. Japan’s presence in the Association shows that it wants engagement with the region at all levels;
Ninthly, The United States and India want to contain China in South Asia and other regions of Asia which are vital for their interests. Japan being ally of the U.S would also desire to keep check on the expansionist designs of China in the region;
Tenthly, currently Japan is desirous of having cordial relations with China. The Japanese Prime Minister, Shinzo Abe, while addressing at the China embassy in Tokyo, in December 2017 invited the President of China to visit Japan. It may reduce the tension in their relations in the perspective of South Asia;
Eleventhly, Pakistan organised multinational naval exercises ‘AMAN-17’ in February 2017. Thirty-seven countries including Russia, China, UK, the US, Russia and Australia participated in the exercises. Japan also took part in the exercises. It indicates that Japan wants to maintain peace on sea routes. It will keep oil supply line to Japan safe;
Twelfthly, the participation of the world powers in AMAN naval exercises also teaches lessons that all the countries want peace at least on waters. It may protect their economic interests. Japan may be the main beneficiary;
Thirteenthly, Afghanistan has received attention in the world politics. The presence of the United States in Afghanistan for last seventeen years has failed to neutralise the power and influence of Taliban. Moreover, the US does not enjoy good relations with Iran. It may increase worry of the US in the region. The failure of the US may not be in the interests of Japan;
Lastly, China’s CPEC initiative possesses politico-economic, socio, cultural and strategic designs. It may increase influence of China in Arabian Sea and South China Sea. Japan may feel its interests in jeopardy and along the new Silk Road.
Though Japan wants to have normal and cordial relations with China, it may not close its eyes to China’s move;
Japan, the world powers and the South Asian countries must leave no stone unturned to ensure peace in the region. Rivalry and confrontation will only cause loss. Consequently, no country may protect and receive its interests peacefully. The protection of one’s interest at the cost of others may only pave the way for the disorder, unrest and hatred in the region.
The writer is an author and has a doctorate in Political Science
Published in Daily Times, March 15th 2018.