About 100 million Pakistani adults lacked access to formal and regulated financial services as of 2016, according to a World Bank report on financial inclusion. Only 2.9% of adults in Pakistan had a debit card, and only 1% of adults used them to make payments. Just 1.4% of adults used an account to receive wages and 1.8% of adults used it to receive government transfers in 2014. Since then, Pakistan has been leading the way in South Asia in digital finance and branchless banking.
According to the latest State Bank statistics on branchless banking (BB) sector, mobile wallets reached a high of 33 million as of September 2017, up 21% over the prior quarter. About 22 percent of these accounts – 7.4 million – are owned by women, up 29% in July-September 2017 over previous quarter. A McKinsey and Co analysis shows that adoption of financial technology (fintech) can help dramatically increase financial inclusion in Pakistan.
Karandaaz Pakistan , a non-profit organization, set up jointly by UK’s Department for International Development and Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, is promoting financial technology in the country. Finja and Inov8 are among the better known fintech startups in the country. Chinese e-commerce giant Alibaba’s Ant Financial’s recent entry in Pakistan is creating a lot of excitement in Pakistan’s fintech community.
Importance of Financial Inclusion:
Access to regulated financial services for all is essential in today’s economy. It allows people and businesses to come out of the shadows and fully participate in the formal economy by saving, borrowing and investing.
Those who lack access to regulated banking services are often forced to resort to work with unscrupulous lenders who trap them in debt at unaffordable rates. Such loans in extreme cases lead to debt bondage in developing countries.
Financial inclusion is good for individuals and small and medium size businesses as well as the national economy. It spurs economic growth and helps document more of the economy to increase transparency.
Status of Financial Inclusion in Pakistan:
About 100 million Pakistani adults lacked access to formal and regulated financial services as of 2016, according to a World Bank report on financial inclusion. Only 2.9% of adults in Pakistan had a debit card, and only 1% of adults used them to make payments. Just 1.4% of adults used an account to receive wages and 1.8% of adults used it to receive government transfers in 2014. Since then, Pakistan has been leading the way in South Asia in digital finance and branchless banking.
Mobile wallets, also called m-wallets, are smartphone applications linked to bank accounts that allow users to make payments for transactions such as retail purchases. According to recent State Bank statistics on branchless banking (BB) sector, mobile wallets reached a high of 33 million as of September 2017, up 21% over the prior quarter. About 22 percent of these accounts – 7.4 million – are owned by women, up 29% seen in Jul-Sep 2017 over previous quarter. Share of active m-wallets has also seen significant growth from a low of 35% in June 2015 to 45% in September 2017.
“The benefits of digital payments go well beyond the convenience many people in developed economies associate with the technology,” says Dr. Leora Klapper, Lead Economist at the World Bank Development Research Group. “Digital financial services lower the cost and increase the security of sending, paying and receiving money. The resulting increase in financial inclusion is also vital to women’s empowerment.”
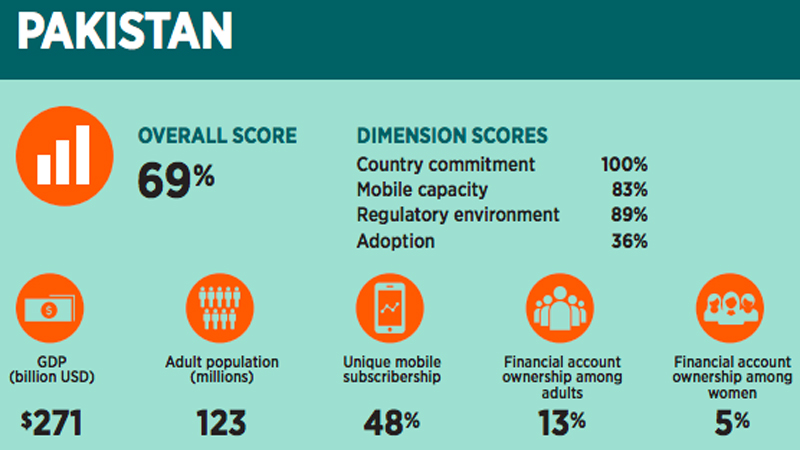
A McKinsey and Co analysis shows that adoption of financial technology (fintech) can help dramatically increase financial inclusion in Pakistan. Pakistan is ranked 16th among 26 nations ranked by Brookings Institution with an overall score of 69% in “The State of Financial and Digital Inclusion Project Report” for 2017. The Internet revolution is enabling rapid growth of financial technology (fintech) for increasing financial inclusion in Pakistan. A McKinsey Global Institute report titled “Digital Finance For All: Powering Inclusive Growth In Emerging Economies” projects that adoption of financial technology (fintech) in Pakistan will add 93 million bank accounts and $36 billion a year to the country’s GDP by 2025. It will also create 4 million new jobs and add $7 billion to the government coffers in this period.
McKinsey report says that “Pakistan has solid digital infrastructure and financial regulation in place and has even had some success in digital domestic-remittance payments”.
Fintech Players in Pakistan:
There are a number of companies, including some startups, offering fintech applications for smartphones that are linked to bank accounts. EasyPaisa operated by Telenor Microfinance is already well established. Among some of the better known startups working to disrupt the financial services sector in Pakistan are Finja and Inov8.
China’s e-commerce giant Alibaba runs a major global e-payments platform Alipay. It also owns Ant Financial which has recently announced the purchase of 45% stake in Pakistan-based Telenor Microfinance Bank.
Telenor Pakistan runs its own e-payments platform EasyPay which will likely link up with Alipay global payments platform after the close of the Ant Financial deal. Bloomberg is also reporting that Alibaba is in serious talks to buy Daraz.pk, an online retailer in Pakistan. These developments are creating a lot of excitement in Pakistan’s fintech and e-commerce communities.
Alibaba and Alipay and other similar platforms are expected to stimulate both domestic and international trade by empowering small and medium size Pakistani entrepreneurial businesses and large established enterprises.
Karandaaz Fintech Promotion:
A key player promoting financial inclusion is Karandaaz Pakistan , a non-profit organization, set up jointly by UK’s Department for International Development and Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. It is providing grants for a number of local initiatives to develop and promote financial technology solutions in Pakistan.
Karandaaz Pakistan is promoting Fintech startups in 5 areas of focus:
1) Access to Financial
services
Credit Scoring Models, Formalize savings through need based products, Digital lending services, and Insurance
2) Payments
Retail payments solutions through QR code, Supply / Value Chain Digitization, Ideas around digitization of online payments and merchant payments
3) E-Commerce
Smoothening of on-boarding process, Enabling Escrow Accounts for a retail merchant, Alternate payment modes other than COD
4) Interoperability
Innovative ideas to address the lack of interoperability among m-wallets
5) Early stage ideas related to:
M-Wallet Use cases, Education of Financial Services through technology, Customer Engagement / Experience, Micro Credit, Digital Savings
Riaz Haq is a Silicon Valley based Pakistani-American analyst and writer. He blogs at www.riazhaq.com
Published in Daily Times, April 2nd 2018.
