As climate warms, S Korea fights new border threat: malarial mosquitoes
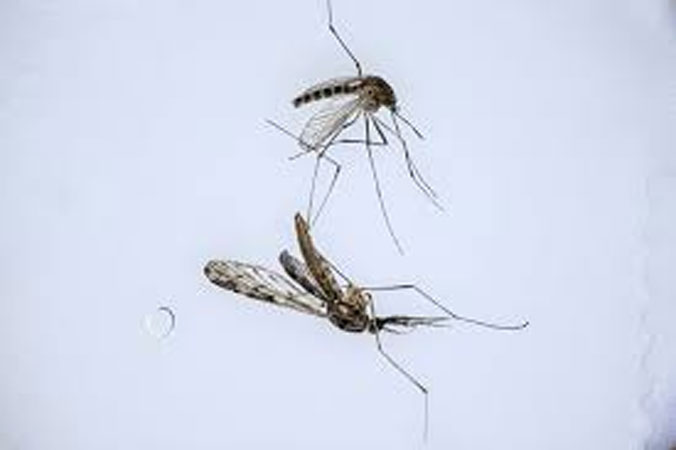

Despite its advanced healthcare service and decades of determined efforts, achieving “malaria-free” status has remained elusive for South Korea, largely thanks to its proximity to the isolated North, where the disease is prevalent.
The South issued a nationwide malaria warning this year, and scientists say climate change, especially warmer springs and heavier rainfall, could bring more mosquito-borne diseases to the peninsula unless the two Koreas, which remain technically at war, cooperate.
The core issue is the DMZ, a four-kilometre-wide no man’s land that runs the full length of the 250-kilometre (155-mile) border.
The demilitarized zone is covered in lush forest and wetlands, and largely unvisited by humans since it was created after the 1953 ceasefire that ended Korean War hostilities.
The heavily mined border barrier area has become an ecological refuge for rare species — an Asiatic black bear was photographed in 2018 — and scientists say it is also an ideal breeding ground for mosquitoes, including malaria carriers that can fly as far as 12 kilometres.
The DMZ has stagnant water plus “plenty of wild animals that serve as blood sources for mosquitoes to feed on in order to lay their eggs”, said Kim Hyun-woo, a staff scientist at Seoul’s Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency.
South Korea once believed it had eradicated malaria, but in 1993 a soldier serving on the DMZ was discovered to have been infected, and the disease has persisted ever since, with cases up nearly 80 percent last year to 747, from 420 in 2022.
“The DMZ is not an area where pest control can be carried out,” Kim Dong-gun, an environmental biology professor at Sahmyook University in Seoul, told AFP.
As mosquito populations increase, more malaria carriers are “feeding on soldiers in the border region, leading to a continuous occurrence of malaria cases there”, he said.
The South Korean health authorities have installed 76 mosquito-tracking devices nationwide, including in key areas near the DMZ. North of the border, malaria is more widespread, with WHO data indicating nearly 4,500 cases between 2021 and 2022, with the country’s extreme poverty and food insecurity likely exacerbating the situation.
Recent Posts
- World
Sir Elton John prepares for the future amid health concerns
Sir Elton John has reportedly made plans for the future, purchasing a property near his…
- World
Iran warns US of strong response to threats of bombing
Iran’s Supreme Leader, Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, warned on Monday that the US would face a…
- World
Microsoft turns 50: leading the charge in AI and cloud computing
Microsoft marks its 50th anniversary this year, celebrating a legacy of innovation in the tech…
- World
Trump confident of tiktok deal before deadline
President Donald Trump expressed confidence in reaching a deal on TikTok before the April 5…
- Pakistan
Sugar import approval delayed as prices stay above government cap
The Pakistani government has yet to approve the import of raw sugar for re-export, amid…
- Lifestyle
Macaulay Culkin opens up about estrangement from his father and its impact
Macaulay Culkin has revealed the painful reason behind his decades-long estrangement from his father, Christopher…
Leave a Comment